DEFENCE
DEFENCE
ARMAMENTS
Iskander | Armenia’s strategic weapon threatening Azerbaijan
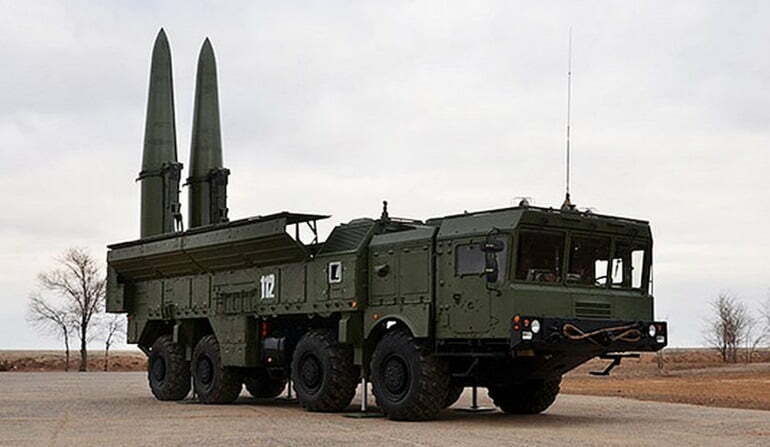

The 9K720 Iskander (NATO reference name: SS-26 Stone) is a mobile short-range ballistic missile system produced and deployed by the Russian Federation.
Iskander missile systems were developed to replace the obsolete OTR-23 Oka systems.
Also read: BREAKING Reports of ballistic missile use by Armenia
In September 2017, KB Mashinostroyeniya (KBM) general designer Valery M. Kashin said there were at least seven types of missiles (and “perhaps more”) for the Iskander, including a guided missile.

The Iskander ballistic missile is superior to its predecessor, the OTR-23 Oka. The Iskander M (Russian Armed Forces Version) system is equipped with two solid propellant single-stage guided missiles (model 9M723K1). Each one in the launcher can be independently launched in a matter of seconds. The mobility of the Iskander launch platform makes a launch difficult to prevent.
Missile targets can be detected not only by satellite and surveillance aircraft, but also by a conventional intelligence center, by an artillery observer or from aerial photographs scanned on a computer. The missiles can be re-targeted during flight. Another unique feature of the Iskander is the optically guided warhead, which can also be controlled by encrypted radio transmission, including those from AWACS or UAV. The missile’s on-board computer receives images of the target, then locks onto the target and descends toward it at supersonic speed.
Boost phase thrust vector control (TVC) is achieved with graphite vanes similar in layout to regular V-2 and Scud tactical ballistic missiles. According to some rumors, during the flight, the missile follows a quasi-ballistic path, performing maneuvers in the final phase of the flight and releasing decoys to penetrate missile defence systems.
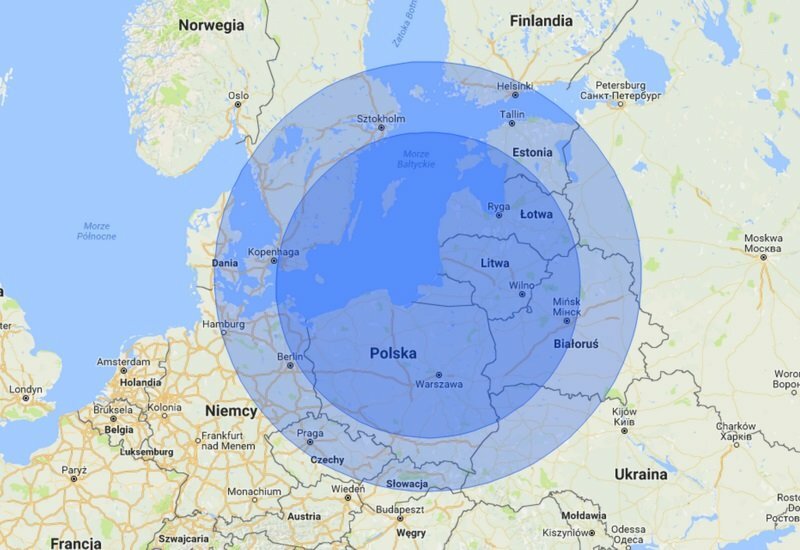
Iskander ballistic missile range
Read also: Hypersonic weapons The latest developments – VIDEO
The Russian Iskander-M travels at a hypersonic speed of 2100–2600 m / s (Mach 6–7). It weighs 4,615 kg, carries a warhead of 710-800 kg, has a range of 500 km and achieves a circular error probable (CEP) of 5-7 meters (when coupled with an optical homing head, 30-70 m in autonomous application). It is rumored that during the flight it can maneuver at different altitudes and trajectories and can turn up to 20 to 30 G to evade anti-ballistic missiles.
Various systems appeared in the rehearsal of the Independence Day parade in September 2016. Four 9K720 Iskander systems were delivered to Armenia under the CSTO agreement, making Armenia the first country (other than Russia) to acquire the system.
In February 2017, the Minister of Defence of Armenia reported to a Russian news agency that the Iskander missiles stationed in Armenia and presented at the military parade in September 2016 were operated by the Armed Forces of Armenia. According to sources, Armenia has a total of 25 units of this ballistic system (Iskander-E with a range of 280 Km).
Read also: TOR M1 | The National Guard’s credible SHORAD
On September 29, Armenian Prime Minister Nicole Pashinyan spoke about whether Yerevan intends to deploy Iskanders against Azerbaijan, in the wake of the use of missile systems and incendiary weapons in Nagorno-Karabakh.

Asked by reporters, Pashinyan confirmed that the security of Armenia and its citizens is a priority for the country.
“Our duty is to prevent the situation from deteriorating and to address the issues of long-term stability,” he told the press.
Earlier, the country’s defence minister had warned that Yerevan might need to use more long-range and powerful weapons systems after Azerbaijan resorted to a longer-range missile solution in the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region.
Read also: Protection of Russian critical infrastructure with upgraded TOR-M2 anti-aircraft system
ARMAMENTS
NEWSLETTER SUBSCRIPTION
Remote Modular Terminal | The US Space Force’s new weapon system
The US Space Force has unveiled its new Remote Modular Terminal (RMT) weapon system. The system has completed its…
ASCANIO | Made-in-Cyprus Mixed Reality training
Technology is advancing at an accelerated pace and so do the training requirements of those holding high-risk positions.
IWI | Introduces Micro Folding Battle Sights to enhance Co-Witness capabilities
IWI (Israel Weapon Industries), a member of the SK Group, has unveiled its new Micro Folding Battle Sights (MFBS).
France | Industries prioritize orders of anti-aircraft missiles
The Armed Forces Ministry of France has instructed industries involved in the production of Aster anti-aircraft and anti-ballistic…
Ecuador | Appeals to International Court of Justice denouncing Mexico
Ecuadorian police stormed the Mexican embassy hours after the Mexican government granted former Vice President…
Remote Modular Terminal | The US Space Force’s new weapon system
The US Space Force has unveiled its new Remote Modular Terminal (RMT) weapon system. The system has completed its…
Latvia | Citizens are asked to turn basements into air raid shelters
Latvian authorities have called on citizens to turn their basements into air raid shelters, causing concern.
HNDGS | Greece – USA bilateral exercise “STOLEN CERBERUS XI” – Photos
From Monday 15 to Friday 26 April 2024, the bilateral exercise “STOLEN CERBERUS XI” took place under the coordination…
ASCANIO | Made-in-Cyprus Mixed Reality training
Technology is advancing at an accelerated pace and so do the training requirements of those holding high-risk positions.


















0 Comments