OPINIONS
OPINIONS

The Cyprus Center for European and International Affairs of the University of Nicosia published the interview given to Dr. Andreas Karyos* by the president of the “Middle East Forum”, Dr. Daniel Pipes**, regarding the recent tensions between Greece and Turkey.
The interview entitled “TURKEY’S” RECONQUESTS “IN THE EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN AND BEYOND” examines, among other issues, the historical background between Greece and Turkey, the impact of Greek-Turkish differences within NATO and the prospects of tripartite relations in the Middle East.
Question: To what extent do you think that historical background affects tensions between Greece and Turkey?
Answer: Historical memory deeply affects Greek-Turkish relations, as it does most international conflicts. In this case, the tensions began on a specific date – Aug. 26, 1071 A.D., at the Battle of Manzikert, when Turks started to invade and conquer most Hellenic lands. Then came Constantinople 1453. In modern times, Smyrna 1922, Istanbul 1955, and Cyprus 1974 maintained this trend. Now, nearly a millennium after Manzikert, the 2019 Turkish-Libyan agreement “on delimitation of the maritime jurisdiction areas in the Mediterranean” continues it by ignoring the normal maritime rights of Greek islands. So too does Erdoğan’s “reconquest” of Hagia Sophia last month. Greeks should worry that, fueled by jihadi motives, Turks seek to conquer all of Hellas and Cyprus.
Also read: Turkish Policy in a few words (Maps)
Question: What does it mean that tension between Turkey and Greece has escalated over the issue of Kastelorizo, a small and isolated island far to the east of the rest of Greece?
Answer: That could be Turkey’s next “reconquest.” In 2012, I wrote an article titled “Kastelorizo – Mediterranean Flashpoint?” and eight years later I worry that the crisis may finally be approaching, perhaps as President Erdoğan seeks popular support in the lead-up to Turkey’s 2023 presidential elections. In particular, I worry about Jack Dulgarian’s scenario of the Erdoğan government invading Kastelorizo, swiftly conquering it, and daring the world to do something. The Hellenic Armed Forces on their own cannot do much. NATO is a paper tiger. Israel will not go to war with Turkey over a remote Greek island with a population of under 500. But if Kastelorizo becomes Turkish at little cost to Ankara, expect the Aegean islands of Greece to be next in its sights.
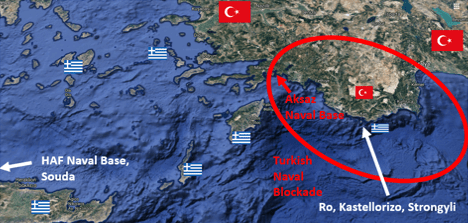
The trouble is, I don’t see how to deter Erdoğan given European weakness and President Trump’s fondness for the Turkish dictator.
Question: What is the impact of the new round of Greek-Turkish disputes on the southern flank of NATO?
Answer: Turkey’s problems with Greece are just a small part of its disputes with other members of NATO, especially Bulgaria, France, Germany, and the United States. This means that, unlike decades past when Athens stood alone against Ankara, Greece is now part of a large, if not full developed or determined grouping. As for the southern flank of NATO, it hardly exists beyond U.S. forces, given general European self-disarmament.
Question: What happens if Erdoğan pushes Syrian and other illegal migrants to Greece in greater numbers than usual?
Answer: In 2015-16, Greece served as a transit zone for Germany, Sweden, and other countries. That situation has ended, and Greece has generally become a final destination. As symbolized by the “living hell” at Camp Moria on Lesbos, it has made itself an undesirable destination. News travels fast and migrants currently in Turkey will less eagerly leave for Greece. This might prompt the Turkish government to pressure them by making their circumstances worse or by forcing them out.
On the other hand, I worry greatly about the Republic of Cyprus, situated just 160 km from Syria and sharing an effectively open border with the Turkish occupied north of Cyprus. Until recently, the governments of Syria and Turkey have mysteriously not targeted Cyprus but that may be changing. Asylum applications increased over four times between 2016 and 2019, from 2,936 to 13,200, with most migrants arriving through the Turkish-occupied north.
Also read: The Turkish provocations of July against Greece and Cyprus
Question: What are the prospects of tripartite partnerships in the Eastern Mediterranean (Greece-Cyprus-Israel, Greece-Cyprus-Egypt)?
Answer: The prospects are excellent for both. Plus, the eastern Mediterranean’s only three democracies share economic interests, especially gas, and security concerns. (By the way, I like Dmitri Shufutinsky’s charming notion of calling the Greece-Cyprus-Israel partnership an “Axis of Antiquity.”) The Eastern Mediterranean Gas Forum is probably even more important. In all, these new groupings graphically show Ankara the price of acting like a rogue state.
Question: Is Ankara doing something about its exclusion from these groupings?
Answer: It toys with the idea of improving relations with Jerusalem but that too much contradicts its Islamist ideology to get far; further, the Israelis have finally grown skeptical. More importantly, Ankara seeks to build alternate partnerships elsewhere, such as with Spain, Italy, various Balkan states, Libya, Qatar, Iran, the Turkic republics, Russia, and China.
Question: How will the agreement between Turkey and Libya play out?
Answer: The agreement has great importance for Libya and beyond. It offers Turks, for the first time in over a century, a direct role in North Africa. One little-noticed aspect of the agreement concerns Fayez al-Sarraj, the head of the GNA faction supported by Ankara, who claims to be of Kuloğlu, or ethnic Turkish heritage; beyond him, the roughly 20 percent of Libyans who share this ethnicity mostly support the Turkish-backed GNA. If this Turkic-oriented approach succeeds in Libya, expect Erdoğan to depend on it more also in the Balkans and maybe also in European countries to which Turks have emigrated.
Also read: Legal analysis of the Exclusive Economic Zone delimitation Agreement between Greece and Egypt
*Andreas Karyos (BA in History & Archaeology, University of Athens; MA in 20th Century European History, Queen Mary, University of London; PhD in Cypriot History, School of Advanced Study, University of London) is teaching faculty in the University of Nicosia (Cyprus),providing education to postgraduate students on Greek-Turkish relations. His research and publication activities focus on various military and political aspects of the Modern History of Cyprus and Greece. Moreover, he offers his expertise at the National Struggle Museum (Cyprus) and he is a member of the board of the Cyprus Society of Historical Studies. Finally, he is a Senior Fellow of the Cyprus Center for European and International Affairs.
**Daniel Pipes, a historian, is the president of the Middle East Forum. A former official in the U.S. departments of State and Defense, he has taught at the University of Chicago, Harvard, Pepperdine, and at the U.S. Naval War College. Mr. Pipes has written sixteen books. His bi- weekly column is published in The Washington Times, National Review, and other publications. His current focus is on the political upheavals in the Middle East. He tweets at @DanielPipes. His website, DanielPipes.org, with an archive of his writings and media appearances, has recorded 70 million page visits since its inception in 2000. More than 11,000 translations of his writings have been published in 37 languages. Both presidents Bush appointed Mr. Pipes to U.S. federal government positions. Al-Qaeda invited him to convert to Islam, Senator Edward M. Kennedy borked him, and Edward Said called him his most horrible name – an “Orientalist.” The Middle East Forum (MEForum.org) is an independent non-profit organization with an annual budget of $4 million which is dedicated to promoting American interests. It produces studies, sponsors activist projects, and makes grants to enable scholars and others to promote the organization’s mission.
NEWSLETTER SUBSCRIPTION
A reluctant alliance? A different approach to French – Serbian defence relations
It has only been a few months since Croatia started receiving the first of the Rafale fighter jets it ordered from France.
The role of SERIOUS GAMES in the development of skills on Defense Standards
In an increasingly complex world, one vital factor for any successful organization is continuous capability building.
Strategy for Building Up Interoperable Defence Capabilities
Based on the current and emerging security threats and challenges in the geostrategic landscape, there is a…
EUROSATORY 2024 | Missile Artillery Solutions from MBDA
With such a large number of interested attendees at MBDA’s pavilion at the Eurosatory 2024 Defence exhibition, the stand reminded of an…
KNDS | Showcases full range of LEOPARD battle tanks at EUROSATORY
KNDS continues to expand its technological advantage in the field of main battle tank development, as we have witnessed at the Defence and…
THEON SENSORS | Distinguishing appearance at EUROSATORY 2024 with new range of products
THEON SENSORS attended the International Defence and Security Exhibition EUROSATORY 2024 as an ambassador of Greek innovation…
Ministry of Defence | Organization of Hellenic EDF Info Day
A Conference entitled “EDF Info Day” is organized in the Amphitheater of the National Gallery on Tuesday, July 9 from 09:00 to 17:00.
ALTUS LSA | Participates in EUROSATORY 2024 with KERVEROS in the foreground
The participation of ALTUS LSA in EUROSATORY 2024 is among the Greek participations of operational significance.
Freddy Beleris | Ιn jail until October
The elected mayor of Heimarra and Member of the European Parliament of New Democracy will remain in prison until October…



















0 Comments