RAFNAR Hellas has announced the official opening of its new state-of-the-art shipyard and headquarters in Lavrio, along with a…

*Athanasios Tsakalos
How are the hypersonic vehicles protected from the extremely high temperatures (over 2,200°C) they develop when flying at speeds exceeding Mach 5? According to the RTX Technology Research Center, a division of RTX corporation (formerly Raytheon Technologies Corporation), the answer is to make them…sweat.
Hypersonic flights promise to revolutionize aeronautics to an unprecedented degree since the “breaking” of the sound barrier in 1947. However, it turns out that going from supersonic to hypersonic is a lot more challenging than going from subsonic to supersonic. One of the biggest challenges is the tremendous heat generated by a body flying in excess of five times the speed of sound.
Also read: Raytheon | A hypersonic missile takes flight
Hypersonic missiles can dart through the atmosphere faster than a mile per second. But at those speeds, the said systems get so hot that many materials would melt.
 The problem
The problem
This means that the carefully designed lines of a hypersonic vehicle, especially its leading edges, will quickly round and distort, completely altering the aerodynamics of the vehicle. This is called ablation, which dulls the vehicle’s leading edge from a triangle to a trapezoid shape.
At these temperatures all but the most “exotic” of materials melt or become inoperable, so there is an increase in drag which ends up slowing the vehicle down, impacting how fast and far it can fly.
The obvious way to avoid this is to cool the outer skin of the vehicle. Unfortunately, with conventional systems, this means adding weight and complexity.
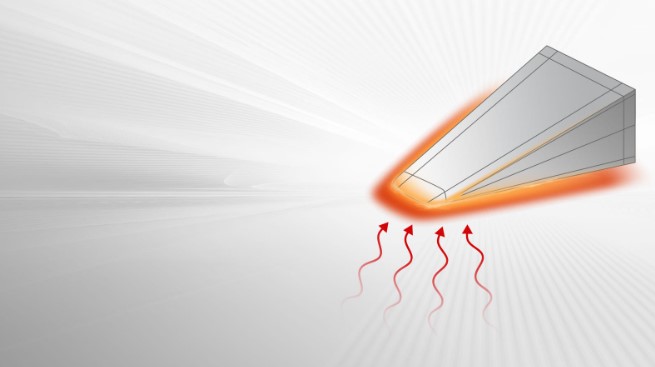 Heatproofing hypersonics
Heatproofing hypersonics
The RTX Technology Research Center has developed proof-of-concept hardware for a heat-proofing hypersonic vehicle that can keep its shape even under the aforementioned temperatures. Under a DARPA (Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency) contract, RTX is looking at cooling hypersonic craft using the same mechanism that humans use to beat heat – sweating.
Hence, to prevent the vehicle from overheating, researchers used a method called transpiration cooling, which mimics the way humans sweat. As such, they drilled thousands of pores into the test hardware and exposed it to extreme temperatures. A liquid inside then surfaced, keeping it within the tolerable temperature to help it maintain its shape.
Specifically, the concept is that the leading edges of a hypersonic vehicle would incorporate a network of micro-channels feeding a liquid to the surface of the skin in a manner similar to human sweat glands. As the liquid reaches the surface, it evaporates, carrying away heat. In this way, the craft can be kept cool enough to maintain its aerodynamics.
 The solution
The solution
According to project team leader John Sharon at the RTX Technology Research Center, predictive modelling and advanced micro-machining were used to create a wedge-shaped test article about the size of a credit card. This was first exposed to a burner rig, which aims a torch fueled by natural gas and oxygen at the test article to mimic changes in temperature that would occur at hypersonic speeds.
Then they conducted more intricate testing at a facility that uses an electrical arc to heat and expand gases to high temperatures and speeds that more closely simulated hypersonic flight conditions.
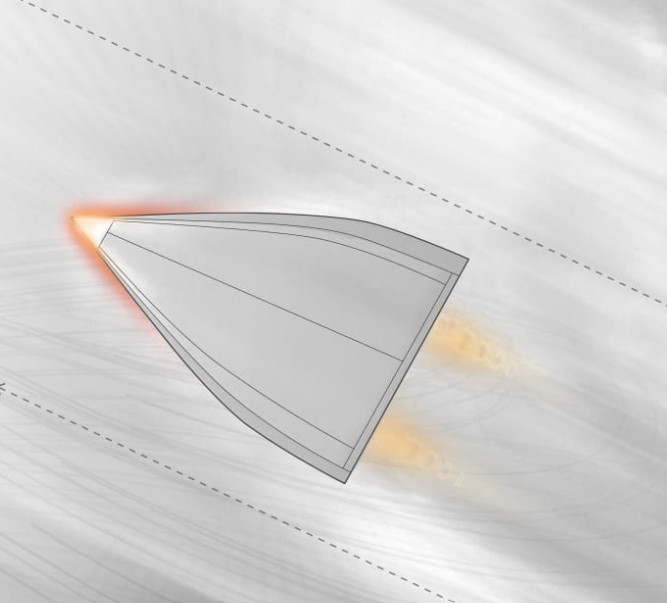 The result
The result
The tests offered preliminary proof that the concept would work, but Sharon said they’ll need more research and refinements before transpiration cooling is ready for use in hypersonic missiles. The remaining challenges include figuring out how to make the channels even smaller and determining whether their findings on a credit card-sized test article would scale to a full-sized hypersonic vehicle.
Should the technique prove successful, it may also be applicable to other problems, like protecting gas turbine blades.
Also read: Hypersonic weapons: The latest developments – VIDEO
READ MORE
IVECO DEFENCE VEHICLES – METLEN | Strategic Alliance for the Hellenic Army’s Military Truck Fleet Modernisation
METLEN and Iveco Defence Vehicles (IDV) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), establishing an exclusive collaboration…
Prisma Electronics | Delivery of the First Systems for the FDI Frigates
Prisma Electronics has successfully delivered the first systems for the FDI frigates, having passed all rigorous acceptance…
HCDI | The Programmatic Horizon of Research and Development Projects for 2025
The Hellenic Defence Innovation Center (HCDI) announced its Programmatic Horizon of Research and Development Projects for 2025, which…
RAFNAR Hellas | New Shipyard in Lavrio, Expansion in Keratea, and New 62-Foot Vessel
RAFNAR Hellas has announced the official opening of its new state-of-the-art shipyard and headquarters in Lavrio, along with a…
IVECO DEFENCE VEHICLES – METLEN | Strategic Alliance for the Hellenic Army’s Military Truck Fleet Modernisation
METLEN and Iveco Defence Vehicles (IDV) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), establishing an exclusive collaboration…
Prisma Electronics | Delivery of the First Systems for the FDI Frigates
Prisma Electronics has successfully delivered the first systems for the FDI frigates, having passed all rigorous acceptance…
Massive Ancient Greek Defensive Wall Unearthed in Croatia
An ancient Greek defensive wall, dating back at least 2,000 years, has been uncovered near the Adriatic coast of Croatia, the…
Airbus | Demonstration of LOAD Against Kamikaze Drones
At the “Unmanned Systems X” trade show held in Bonn, Germany, on 25-26 March, Airbus introduced its new unmanned air defence system, LOAD.