The Ministry of National Defence, reaching the end of 2024, feels the obligation to thank the 103 donors, whose donations were a valuable…

Mr. Ioannis Ioannidis, the man who leads Deloitte Cyprus’ Cyber Risk Services, participated in the “Armed and Security Forces Synergies” session during the BATTLEFIELD ReDEFiNED 2023 International Conference held in Cyprus.
In his presentation entitled “Cyberwarfare – The unseen battlefield”, Mr. Ioannidis referred to the most modern form of warfare and its effects, cyberwarfare.

First, Mr. Ioannidis pointed out the main types of cyberwarfare with reference to “phishing” – phishing attacks aimed at stealing or damaging sensitive data by tricking people into revealing personal information such as passwords and credit card numbers – and ransomware – a type of malware or malicious software that threatens the victim by destroying or blocking access to crucial data or systems until a ransom is paid. In fact, these are methods that have evolved into the most rampant forms of cybercrime.
Furthermore, Mr. Ioannidis referred to the term “hacktivism”, which is widespread due to the recent developments in Ukraine. It is a method of activism on the Internet through the use of malicious software, which aims to incite political disobedience and protest (Protestware) for the promotion of a political agenda or social change.
The speaker then decoded the objectives of such malicious attacks as follows:
- Disruption of critical services
- Achieving political and psychological results through propaganda and fear tactics
- Derailment of military transport and humanitarian aid
- Disruption of public access to services and media
- Stealing information and data to extract information or economic value
Also read: Medusa ransomware | Claims responsibility for cyberattack on the Open University of Cyprus
The presentation continued with Mr. Ioannidis placing emphasis on a particularly critical aspect of cyber attacks: supply chain attacks.
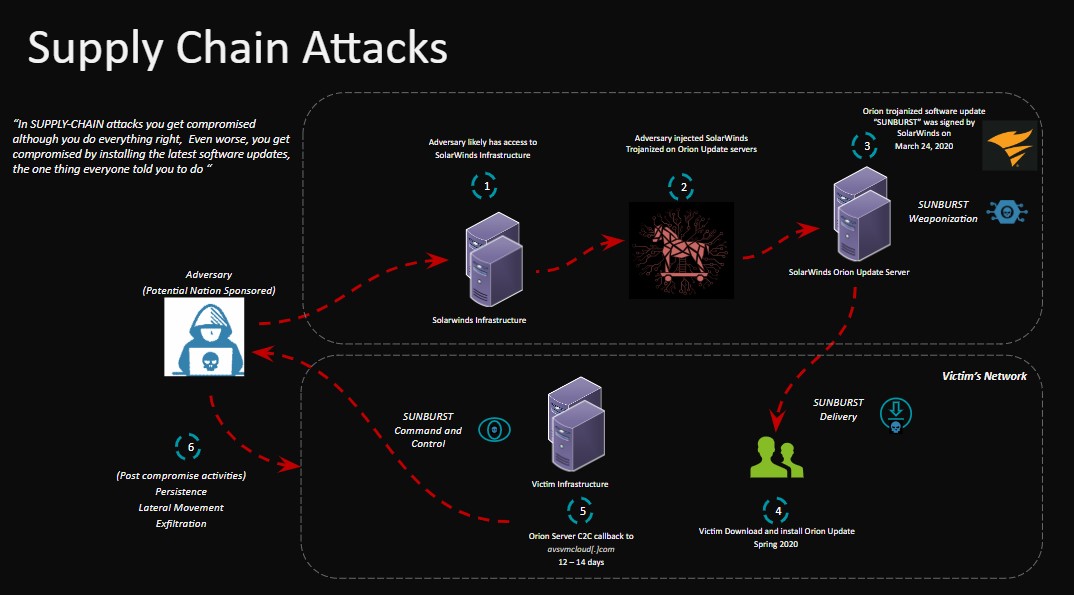
Supply chain attacks are an emerging threat, targeting the software of outside developers and suppliers. In this way, attackers seek to gain access to source codes, create processes or update mechanisms by infecting legitimate applications to distribute malware.
For example, by delivering viruses or other malware through a provider, an infected USB drive can enter a company and, during its use, steal passwords.
Also read: Cyprus | Government websites down due to water leak – The value of Data Centers
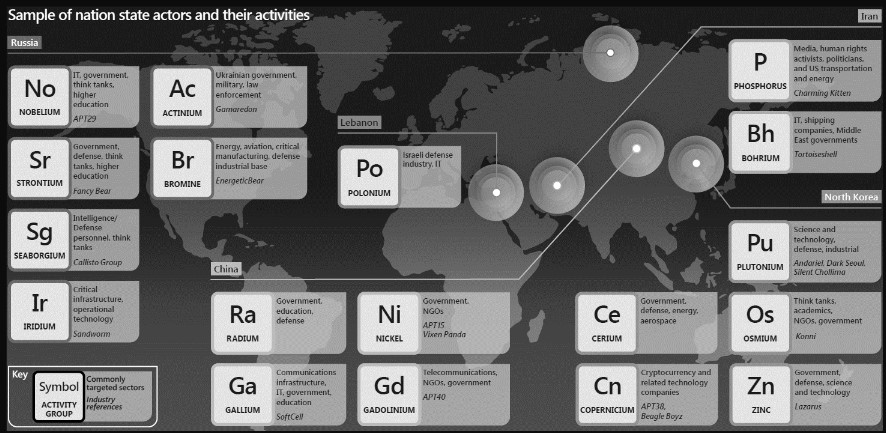
In addition, Mr. Ioannidis made special mention of cyber attack activities at the state level with the obvious purpose of promoting national interests. These mainly concern:
- Intellectual property theft
- Espionage
- Surveillance
- Sponsorship of operations
- Credential theft
- Destructive attacks
According to Mr. Ioannidis, targets of cyber attacks are sectors such as Information Systems, Non-Governmental Organizations, Education, Transport, Governments, and Health.
Finally, Mr. Ioannidis attempted to get across to the delegates the scope of the severity of the impact of such malicious activities in terms of public safety by referring to the Blackout in Kyiv in 2016, where 3 million people were left without power due to a modular, automated and widespread cyber attack.
Also read: Ukraine | Massive cyberattack on government websites
READ MORE
BATTLEFIELD ReDEFiNED 2024 | The premier Defence and Security Conference Successfully Concludes in Cyprus – Photos
The International Defence and Security Conference “BATTLEFIELD ReDEFiNED 2024” was successfully concluded on Friday, 13, December 2024…
BATTLEFIELD ReDEFiNED 2024 | The Major Defence and Security Conference has Started in Cyprus – Photos
The defence and security conference, BATTLEFIELD ReDEFINED 2024, started today and is taking place in Nicosia…
Ground Warden Vehicle | MBDA’s cutting-edge solution with missiles, loitering munitions and drones – Video & Photos
During the EUROSATORY 2024 Defence and Security exhibition, MBDA presented the Ground Warden Vehicle solution, an innovative…
A World in Conflict | 2024 Leaves Behind Wars and an Unrelenting Tide of Violence
As 2024 comes to an end, the global geopolitical stage remains engulfed by a myriad of conflicts ranging from armed conflicts…
Ministry of National Defence | Thank-you announcement for the 103 donors who offered 26 million euros in 2024 to the Hellenic Armed Forces
The Ministry of National Defence, reaching the end of 2024, feels the obligation to thank the 103 donors, whose donations were a valuable…
Syria | Former Rebels and Foreign Jihadists were Promoted to Army Officers
Former rebels have been promoted to officers in the future Syrian army under a decree by the country’s new leader…
Russia – Ukraine | Prisoner Εxchange Βrokered by the United Arab Emirates
Russia and Ukraine conducted a prisoner exchange today, with each side releasing 150 prisoners of war, according…
Embraer | Signing of a Contract to Supply two C-390 Transport Aircraft to an Undisclosed Customer
Brazil’s Embraer announced on Friday that it has signed a contract to sell two C-390 Millennium transport aircraft…