DEFENCE
DEFENCE

The Russian-made SHOrt-Range Air Defence system (SHORAD) was designed in the 1980s to provide point defence. It was launched in 1986 and to date the system has been produced in various versions, with TOR-M2MK which Armenia recently bought and TOR-M2DT Artic being the most recent.
TOR M1 or SA-15 “Gauntlet” (by NATO coding) was delivered to the National Guard by the Greek Army (which is also a system user) in 1999, following the well-known issue regarding the transfer of the russian long-range S-300 PMU 1 anti-aircraft system to Crete. The S-300 misiles were bought by the Government of Cyprus but installed in Crete instead of Cyprus after Turkey threatened Cyprus and Greece with war.
TOR M1 is an all-weather, anti-aircraft system based on a tracked vehicle. The system can effectively engage a number of targets, including regular aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV’s), cruise missiles and precision guided ammunition.
The system has increased survivability in the modern battlefield due to its construction, having the firing radar and target lock built into each launcher, as well as the possibility of rapid deployment and firing. In addition, the system has strong protection against electromagnetic interference (ECM) as well as protection from nuclear radiation and biological-chemical (NBC) agents on the crew inside the vehicle.
Specifications:
- Manufacturer: ALMAZ-Antey
- Maximum Missile Range (9M331): 12 Km
- Target engagement elevation: 10m-6000m
- Missile Speed: 850 m / s
- Maximum Missile Maneuverability: 30 G
- Maximum Target Lock Range: 24 Km
- Maximum number of targets that can be monitored simultaneously: 9
- 9M331 Missiles per Combat Vehicle 9A331-1: 8
- CV 9A331-1 crew: 4 (Unit Commander, two console operators and driver)
- CV 9A331-1 vehicle range: 500 Km
Typical TOR M1 battery composition:
A battery normally consists of 3 Combat Vehicles (CV) 9A331-1, each carrying 8 9M331 missiles, 1 Battery Command Post-BCP 9S737M, special transport-loading vehicles (Ural 4320 Transport Launch Vehicle) 9T244, transport vehicles (Transport Vehicle-TV) 9T245 and mobile spare parts vehicles.
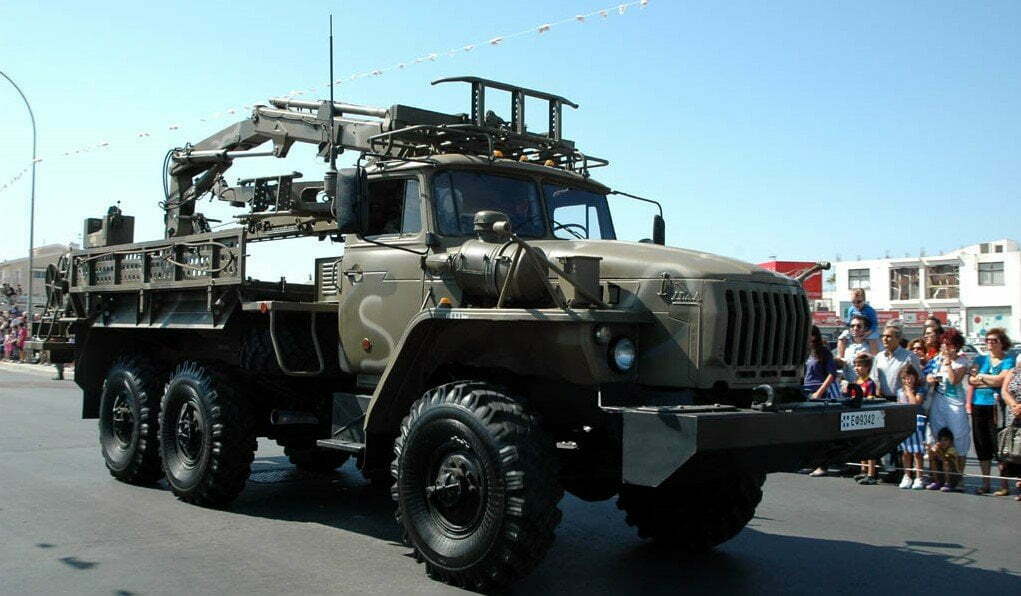

Ural 4320 Transport Launch Vehicle 9T244
TOR M1 can operate either in pairs or autonomously. Each CV 9A331-1 combat vehicle can monitor up to 9 targets simultaneously and engage 2 under certain conditions, thus enabling the artillery to simultaneously engage up to 6 targets.
The National Guard has 6 TOR M1 CV 9A331-1 and 2 TOR M1 BCP 9S737M combat vehicles divided into 2 Batteries.
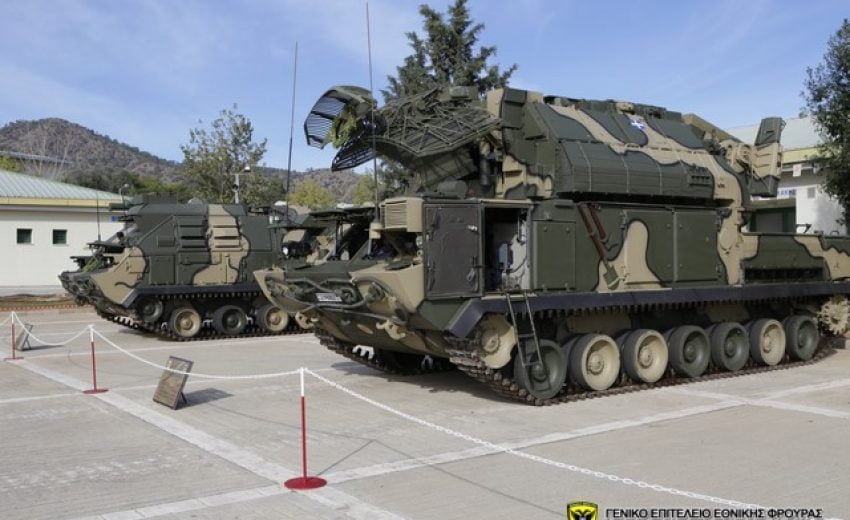

National Guard’s Battery Command Post (BCP) 9S737M and Combat Vehicle CV 9A331-1
Operational Evaluation
In October 2000, 1 TOR M1 system of the 181st Mobilised Guided Missile Battalion of the National Guard allegedly locked 2 Turkish RF-4E reconnaissance aircraft which tried to photograph the Andreas Papandreou air base during the 2000 “Nikiforos-Toxotis” exercise. Since then, the system, along with the rest of the National Guard systems, has been involved in various exercises between the National Guard and other countries. The systems of the National Guard, staffed by experienced and well-trained personnel, have proved particularly “lethal” in the fields amongst others of the “ONISILOS-GIDEON” exercises between the National Guard and the Israeli Air Force from 2014 onwards.
Lima | Ukraine’s Game-Changing Jammer Against Russian Glide Bombs
Ukraine has deployed a new electronic warfare system that is reshaping the dynamics of aerial combat on the battlefield.
Anduril | Introduction of the Torpedo-Inspired Underwater Kamikaze Drone Copperhead
Anduril has unveiled a torpedo-inspired underwater attack drone in response to emerging maritime threats.
Gizelis S.A. Enters the Defence Sector | Strategic Partnership with Israeli Company Aharon Yosef – אהרון יוסף
Gizelis S.A. has officially announced its entry into the defence industry through a strategic partnership with the Israeli company Aharon Yosef.
Greece | Declaration of EEZ in the Ionian Sea and Presentation of Maritime Spatial Map
In an initiative with significant geopolitical and economic implications, Greece has declared an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) in the Ionian Sea…
Lima | Ukraine’s Game-Changing Jammer Against Russian Glide Bombs
Ukraine has deployed a new electronic warfare system that is reshaping the dynamics of aerial combat on the battlefield.
Latvia | Withdrawal from the Ottawa Treaty Banning Anti-Personnel Mines
Latvia’s parliament has approved the country’s withdrawal from the Ottawa Convention banning anti-personnel mines, citing the need to bolster national…
THEON | Publication of the Annual Financial Report for 2024
THEON INTERNATIONAL Plc (THEON) has recently published its Annual Financial Report for 2024, with the results reflecting a very strong…
Cyprus | Major General Bewick Sworn in as New British Base Commander
Major General Tom Bewick was officially sworn in as the new Area Manager of the British Bases in Cyprus during a ceremony…
OPINION | TIME OF DECISION FOR EUROPEAN DEFENCE AND SECURITY
Although the defence, security, and protection of the territorial integrity and independence of the member states of the European Union (EU) remain primarily…














0 Comments